Publish/Subscribe messaging model using RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ, a widely used open-source message broker, is heavily utilized by businesses implementing the microservices paradigm. For organizations embracing this approach, RabbitMQ functions as a streamlined tool that enables smooth connection and communication among their services. This article is intended to clarify the steps involved in integrating pub/sub messaging into applications.
Prerequisites
I presume you have already configured RabbitMQ on your system. If not, you can refer to this blog post for the setup instructions. https://codenotfound.com/rabbitmq-download-install-windows.html
Terminologies
-
Producer: An application that generates and dispatches messages to the RabbitMQ broker, publishing these messages to the exchange.
-
Exchange: A RabbitMQ component responsible for routing messages to queues. RabbitMQ supports multiple exchange types.
- Direct : 1:1 messaging to qeueue
- Fanout: Broadcasting messages to all the queues bound to the exchange.
- Topic : A message sent with a particular routing key will be delivered to all the queues that are bound with a matching binding key. In this article we will talk about Topic Exchange in detail.
-
Queues: It stores the messages.
-
Bindings: It binds exchange and queue. Based on the binding the exchange publishes the message to specific queue.
-
Consumer: An application responsible for receiving and handling messages from a queue.
The pub/sub pattern operates in the following manner: the publisher dispatches a message to the message broker, which subsequently directs the message to all subscribers expressing an interest in receiving it. Subscribers and publishers need not be aware of each other. The message broker acts as middleware, effectively decoupling the two.
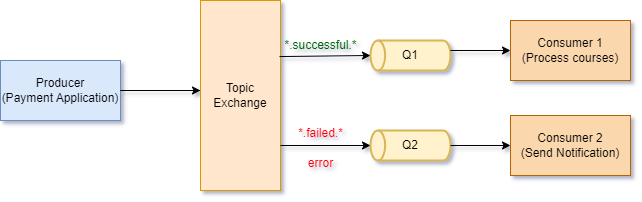
Consider a scenario in which a user purchases a Learning Path with multiple courses from Udemy. After the user places the order, a payment request is transmitted to the payment gateway.
In this context, the payment request can result in three distinct statuses: successful, unsuccessful, or an error state, each with its unique implications. If the payment is successful, the objective is to allocate the courses to the user. In the event of a payment failure or an error occurrence, the goal is to inform the user and provide a link to address the payment issue.
In this scenario, three applications are involved: the payment gateway (on the Udemy site), the Course Assignment application, and the Notification Application. The payment gateway will publish a message to an exchange, incorporating the payment status as the routing key. The exchange, utilizing the routing key/binding mechanism, will route messages to the appropriate queues based on the payment status.
Setup RabbitMQ connection
Declare Exchange
Declare paymentexchange with Topic as ExchangeType.
Declare Queue
Define a queue for the Payment Successful status and another queue for Failure/Error notifications.
Bind Queue
Establish a binding between a queue, a routing key, and an exchange. A queue can be bound to either a single or multiple routing keys.
For example, the queue named payment_success is bound to the routingkey=*.successful.*. The following are some examples of routing keys that would be directed to this specific queue.
- payment.successful.assign.courses
- successful.assign.courses
- payment.order.successful.assign.courses
The notification queue is bound to routingKey=*.failed.*. Consequently, messages with the following routing keys would be forwarded to the queue:
- payment.failed.notify
- failed.revert.demo
- failed
The notification queue is also bound to routingKey=error. In this scenario, only the routing key error is permitted.
Publish message by publisher
Declare Consumer
In the AssignCourses application, establish a consumer that listens to the payment_success queue. Upon receiving a message, the application will proceed to assign courses to the user.
Within the Notification application, define a consumer that actively monitors the notification queue. Upon receiving a message signaling payment failure or an error, the application will promptly notify the user, providing a link to rectify the payment for the order.
Conclusion
This approach allows us to implement a pub/sub messaging model by utilizing RabbitMQ's topic exchange for seamless intercommunication between applications.

